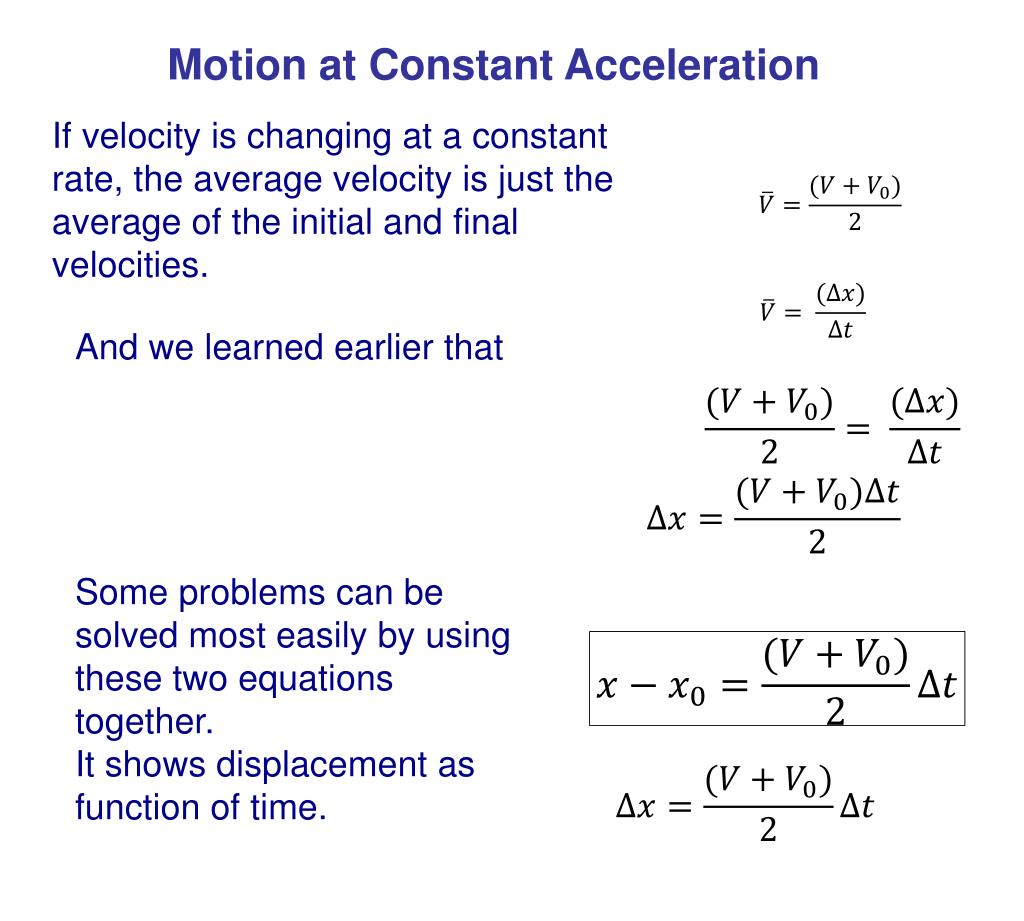
Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration . Change your speed or change your direction—or change both. Web acceleration, denoted by the symbol a →, is a vector quantity defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect. Web in part (a) of the figure, acceleration is constant, with velocity increasing at a constant rate. Web since velocity is a speed and a direction, there are only two ways for you to accelerate: Web explain that the acceleration arrow points in the direction opposite the velocity because the velocity is getting smaller, i.e., the. The si unit for acceleration is. Web acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. In symbols, average acceleration is a= δv/δt. Web equation 2.5.5 reflects the fact that, when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities.
from www.slideserve.com
In symbols, average acceleration is a= δv/δt. Web acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. Web explain that the acceleration arrow points in the direction opposite the velocity because the velocity is getting smaller, i.e., the. Web since velocity is a speed and a direction, there are only two ways for you to accelerate: Web in part (a) of the figure, acceleration is constant, with velocity increasing at a constant rate. The si unit for acceleration is. Web acceleration, denoted by the symbol a →, is a vector quantity defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect. Change your speed or change your direction—or change both. Web equation 2.5.5 reflects the fact that, when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities.
PPT Unit 3 Kinematics Equations PowerPoint Presentation, free
Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Web acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. The si unit for acceleration is. Web acceleration, denoted by the symbol a →, is a vector quantity defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect. Web explain that the acceleration arrow points in the direction opposite the velocity because the velocity is getting smaller, i.e., the. Change your speed or change your direction—or change both. Web equation 2.5.5 reflects the fact that, when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. In symbols, average acceleration is a= δv/δt. Web acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. Web since velocity is a speed and a direction, there are only two ways for you to accelerate: Web in part (a) of the figure, acceleration is constant, with velocity increasing at a constant rate.
From www.youtube.com
AP Physics Workbook 1.F Constant Velocity YouTube Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Web explain that the acceleration arrow points in the direction opposite the velocity because the velocity is getting smaller, i.e., the. Change your speed or change your direction—or change both. In symbols, average acceleration is a= δv/δt. Web in part (a) of the figure, acceleration is constant, with velocity increasing at a constant rate. Web acceleration, denoted by the symbol. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Physics Chapter 2 Notes PowerPoint Presentation, free download Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Change your speed or change your direction—or change both. The si unit for acceleration is. Web equation 2.5.5 reflects the fact that, when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. Web in part (a) of the figure, acceleration is constant, with velocity increasing at a constant rate. Web since velocity is a. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From www.youtube.com
Velocity and Acceleration Constant Velocity YouTube Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Web acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. Web equation 2.5.5 reflects the fact that, when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. Web in part (a) of the figure, acceleration is constant, with velocity increasing at a constant rate. The si unit for acceleration is. Web since velocity is a. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From www.youtube.com
How to Calculate Acceleration From a Velocity Time Graph Tutorial YouTube Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Web since velocity is a speed and a direction, there are only two ways for you to accelerate: Web explain that the acceleration arrow points in the direction opposite the velocity because the velocity is getting smaller, i.e., the. Change your speed or change your direction—or change both. Web acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. The si unit. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From studylib.net
Centripetal Acceleration Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Web acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. Web since velocity is a speed and a direction, there are only two ways for you to accelerate: Change your speed or change your direction—or change both. In symbols, average acceleration is a= δv/δt. Web acceleration, denoted by the symbol a →, is a vector quantity defined as the rate of. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From www.pinterest.ph
Forceacceleration relationship Acceleration, Exam study tips Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Web equation 2.5.5 reflects the fact that, when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. The si unit for acceleration is. Web acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. Web in part (a) of the figure, acceleration is constant, with velocity increasing at a constant rate. In symbols, average acceleration is. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration In symbols, average acceleration is a= δv/δt. Web explain that the acceleration arrow points in the direction opposite the velocity because the velocity is getting smaller, i.e., the. Web in part (a) of the figure, acceleration is constant, with velocity increasing at a constant rate. Change your speed or change your direction—or change both. Web acceleration, denoted by the symbol. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration PowerPoint Presentation, free Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Web since velocity is a speed and a direction, there are only two ways for you to accelerate: Web equation 2.5.5 reflects the fact that, when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. Change your speed or change your direction—or change both. Web acceleration, denoted by the symbol a →, is a. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From www.doubtnut.com
The displacementtime graph of a moving particle with constant acceler Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration In symbols, average acceleration is a= δv/δt. The si unit for acceleration is. Web explain that the acceleration arrow points in the direction opposite the velocity because the velocity is getting smaller, i.e., the. Change your speed or change your direction—or change both. Web since velocity is a speed and a direction, there are only two ways for you to. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From slideplayer.com
Introduction to Motion ppt download Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Web acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. Web equation 2.5.5 reflects the fact that, when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. Web explain that the acceleration arrow points in the direction opposite the velocity because the velocity is getting smaller, i.e., the. Web in part (a) of the figure,. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From www.youtube.com
VelocityTime Graphs Part 2 Graphs with Changing Velocity IB Physics Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Web acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. Change your speed or change your direction—or change both. Web in part (a) of the figure, acceleration is constant, with velocity increasing at a constant rate. Web explain that the acceleration arrow points in the direction opposite the velocity because the velocity is getting smaller, i.e., the. Web acceleration, denoted by. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 4 Accelerated Motion in a Straight Line PowerPoint Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Change your speed or change your direction—or change both. Web acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. In symbols, average acceleration is a= δv/δt. Web equation 2.5.5 reflects the fact that, when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. Web since velocity is a speed and a direction, there are only. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From www.teachoo.com
Velocity Time Graph Meaning of Shapes Teachoo Concepts Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Change your speed or change your direction—or change both. In symbols, average acceleration is a= δv/δt. Web acceleration, denoted by the symbol a →, is a vector quantity defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect. Web in part (a) of the figure, acceleration is constant, with velocity increasing at a constant rate. Web explain that the acceleration. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From study.com
Using Velocity vs. Time Graphs to Describe Motion Video & Lesson Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Web equation 2.5.5 reflects the fact that, when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. Change your speed or change your direction—or change both. Web acceleration, denoted by the symbol a →, is a vector quantity defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect. The si unit for acceleration is.. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From mmerevise.co.uk
Motion Graphs Questions and Revision MME Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Web acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. In symbols, average acceleration is a= δv/δt. Change your speed or change your direction—or change both. Web in part (a) of the figure, acceleration is constant, with velocity increasing at a constant rate. The si unit for acceleration is. Web acceleration, denoted by the symbol a →, is a vector quantity. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Physics 114A Mechanics Lecture 2 (Walker 2.12.3) Position and Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Web acceleration, denoted by the symbol a →, is a vector quantity defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect. Web explain that the acceleration arrow points in the direction opposite the velocity because the velocity is getting smaller, i.e., the. Web equation 2.5.5 reflects the fact that, when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Kinematics Equations PowerPoint Presentation ID2157638 Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration Web acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. The si unit for acceleration is. Web since velocity is a speed and a direction, there are only two ways for you to accelerate: Web explain that the acceleration arrow points in the direction opposite the velocity because the velocity is getting smaller, i.e., the. Web acceleration, denoted by the symbol. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.
From studyzonevirtuality.z5.web.core.windows.net
How To Find Acceleration Kinematics Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration In symbols, average acceleration is a= δv/δt. Web acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. Web in part (a) of the figure, acceleration is constant, with velocity increasing at a constant rate. The si unit for acceleration is. Web explain that the acceleration arrow points in the direction opposite the velocity because the velocity is getting smaller, i.e., the.. Constant Velocity Changing Acceleration.